使用
我先直接分享一下我是如何使用CompletableFuture的吧,以下仅为示例,具体实现以业务情况自行改造
1
2
3
4
|
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>(1000);
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Integer> concurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
IntStream.range(0,1000).forEach(resultList::add);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| public List<R> sendAsyncBatch(List<P> list, Executor executor, TaskLoader<R,P> loader) {
List<R> resultList = Collections.synchronizedList(Lists.newArrayList());
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(list)) {
Executor finalExecutor = executor;
CollUtil.split(list, 50)
.forEach(tempList -> {
CompletableFuture[] completableFutures = tempList.stream()
.map(p -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
return loader.load(p);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}, finalExecutor)
.handle((result, throwable) -> {
if (Objects.nonNull(throwable)) {
} else if (Objects.nonNull(result)) {
} else {
}
return result;
}).whenComplete((r, ex) -> {
if (Objects.nonNull(r)) {
resultList.add((R) r);
}
})
).toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new);
CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutures).join();
System.out.println(resultList.size());
});
}
return resultList;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TaskLoader<T,P> {
T load(P p) throws InterruptedException;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
ExecutorService executorService = BaseThreadPoolExector.queueExecutor(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(500));
AsyncTask<Integer, Integer> asyncTask = new AsyncTask();
List<Integer> list = asyncTask.sendAsyncBatch(resultList, executorService, new TaskLoadImpl());
|
- CompletableFuture为我们提供更直观、更优美的API。
- 在“多个任务等待完成状态”这个应用场景,在遇到异常的情况下我们不需要去手动的抛异常,以免错误处理细节导致阻塞
- CompletableFuture也可以定制执行器
但是他也是有缺点的,我个人感觉他的API有点多,看的时候让人眼花。
短短十几行的代码,看到了很多API supplyAsync、handle、whenComplete、allOf
之后我们还会用到runAsync、 thenApply、thenCompose等等其他的。
什么是CompletableFuture?
异步编程,利用多线程优化性能这个核心方案得以实施的基础
他的目的也很简单,同一个CPU上执行几个松耦合的任务,充分利用CPU核数,实现最大化吞吐量,避免因为阻塞造成等待时间过长;
要区分并发与并行的区别
我们还需要特别的注意这两个概念不能混淆
并发:在一个CPU上串行执行
并行:多个CPU上同时执行任务
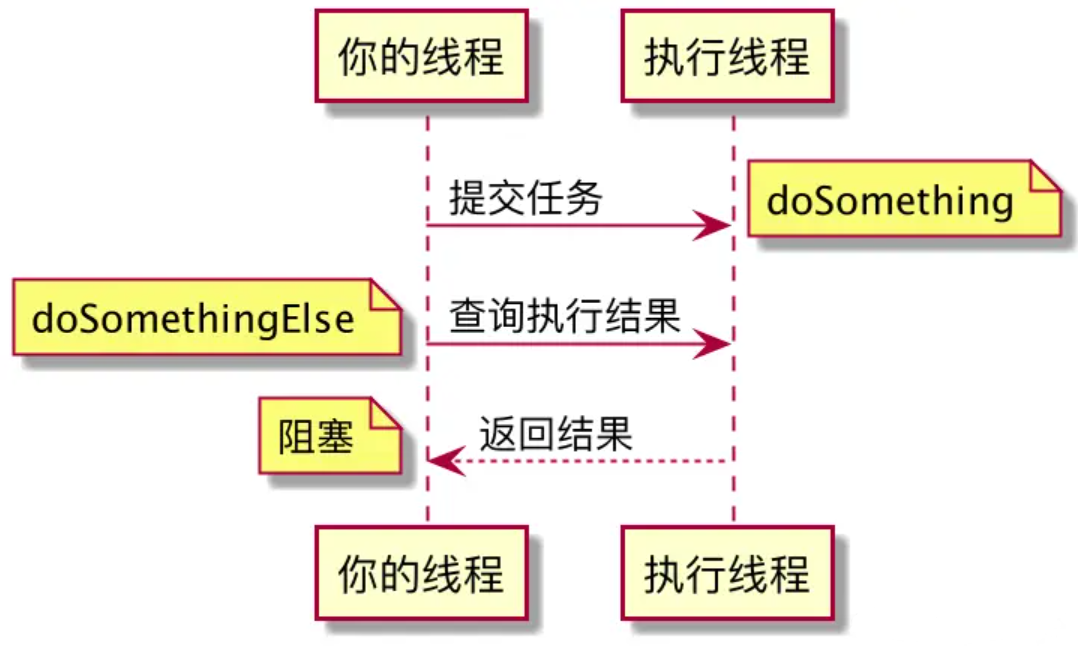
Future接口
CompletableFuture主要继承了Future接口,但是他比Future接口丰富的很多
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
|


可以看到Future接口的局限性,主要是用起来不省事
举个例子:A线程执行完之后通知B线程执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| ExecutorService executorService = BaseThreadPoolExector.calculateExecutor();
Future<String> futureA = executorService.submit(() -> Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(futureA.get());
if (futureA.isDone()){
Future<String> futureB = executorService.submit(() -> Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(futureB.get());
}
executorService.shutdown();
|
这里我们就需要查询futureA.isDone()结果,然后再去执行B线程的业务
而 CompletableFuture 操作起来就便捷很多了
1
2
3
4
| CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> Thread.currentThread().getName(), executorService)
.thenApply(s -> Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
|
supplyAsync执行完成之后,再去执行thenApply
没有繁琐的手工维护线程的工作,给任务分配线程的工作也不需要我们关注
错误处理细节,避免造成阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
new Thread(() ->{
try {
completableFuture.complete(10/0);
}catch (Exception ex){
completableFuture.completeExceptionally(ex);
}
}).start();
try {
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
注意到catch里面的completeExceptionally函数了吧,这个主要的作用就是为了抛出异常,如果缺少了他,就会造成completableFuture.get()一直处于等待造成阻塞,与此同时,没有为我们抛出异常信息。
所以CompletableFuture的API优美之处又要体现出来了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int kk = 10 / 0;
return kk;
}).handle((result, throwable) -> {
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage());
return result;
}).whenComplete((result ,throwable) -> System.out.println(result));
|
supplyAsync配合着 handle 和 whenComplete,将异常和结果进行处理
handle 和 whenComplete 的区别
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {
return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(
BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {
return uniHandleStage(null, fn);
}
|
whenComplete是BiConsumer也就是直接消费不返回值,不对结果产生影响
如果单独使用whenComplete的时候,没有进行抛出异常的处理会造成阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int kk = 10 / 0;
return kk;
})
.whenComplete((r, ex) -> {
if (Objects.nonNull(ex)) {
System.out.println("whenComplete>>>" + ex.getMessage());
}
})
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
System.out.println("exceptionally>>>" + throwable.getMessage());
return null;
});
|
handle是BiFunction也就是需要返回值,对结果产生影响
需要注意的是,在handle中对结果修改,要避免结果对象为空,如果没有判断直接进行操作会出现空指针异常造成阻塞
在这里出现空指针异常,如果没有exceptionally将异常抛出,则会造成阻塞
了解API
欲善其功,必先利其器
我们主要从这三种关系下手去了解和使用API 涉及接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| CompletionStage<R> thenApply(fn);
CompletionStage<R> thenApplyAsync(fn);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(action);
CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(action);
CompletionStage<R> thenCompose(fn);
CompletionStage<R> thenComposeAsync(fn);
|
thenApply函数里参数入参Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,这个接口里与 CompletionStage 相关的方法是 R apply(T t),这个方法既能接收参数也支持返回值,所以 thenApply函数出参的是CompletionStage<R>。
thenAccept类型函数入参Consumer<? super T> action是一个消费类型的,回参是CompletionStage<Void>所以thenAccept类型函数不会有返回值。
thenRun函数入参Runnable action,回参CompletionStage<Void>,所以既不能接收参数也不支持返回值。
thenCombine函数入参CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,回参CompletableFuture<V>是支持返回值的,他的作用主要使用BiFunction处理两个阶段的结果
我们只需要注意他的入参、回参和函数后缀就能够区分出他们的不同
CompletableFuture中的串行化关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
return Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":小郭";
},executorService).thenApply(s -> {
return s + "拿茶叶";
}).thenApply(a ->{
return a + ",泡茶去";
}).handle((result, ex) ->{
if (ex != null){
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
return result;
}).whenComplete((r, ex) ->{
System.out.println(r);
});
task1.join();
|
执行结果:
1
| pool-1-thread-1:小郭拿茶叶,泡茶去
|
可以看到,是按照之上而下的顺序去执行的supplyAsync、thenApply、thenApply 如果第二阶段任务没有拿到第一阶段的结果,他就会等待
CompletableFuture中的汇聚AND关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| CompletableFuture<Integer> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
int t = new Random().nextInt(30);
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task1=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
int t = new Random().nextInt(30);
try {
Thread.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task2=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = task1.thenCombineAsync(task2, Integer::sum);
task3.join();
|
等待task1和task2执行完成,task再进行处理后续结果
CompletableFuture中的汇聚OR关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| CompletableFuture<Integer> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
int t = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
Thread.sleep(t * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task1=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
int t = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
Thread.sleep(t * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task2=" + t);
return t;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> task3 = task1.applyToEither(task2, s ->s);
task3.join();
|
谁先执行完先输出谁,如果相同时间执行完,则一起
实现List任务并行执行的方式
- 并行流进行操作
- 使用CompletableFuture发起异步请求,最后使用join等待所有异步操作结束
为了更好的发挥出CompletableFuture,需要采用定制的执行器
那这两个如何选择?
- 进行计算密集型,并且没有I/O操作,推荐使用Sream并行流,没必要创建更多的线程,线程过多反而是一种浪费
- 涉及I/O等待的操作,CompletableFuture的灵活性会更高
总结
- 在执行比较耗时的业务操作时候可以使用异步编程来提高性能,加快程序的处理速度
- 在处理异常机制的时候,往往是让我们很头痛的,担心线程中出现的异常没有及时捕获,造成程序的阻塞或者其他方面的影响,CompletableFuture 提供了优秀的异常管理机制。
- CompletableFuture 还提供了 串行、聚合、优先输出的函数,更贴切业务需求做出最好的选择。
后续将会通过新文章继续补充~